Contents
Esophagitis
Understanding, Diagnosing & Treating Oesophageal Inflammation
Overview
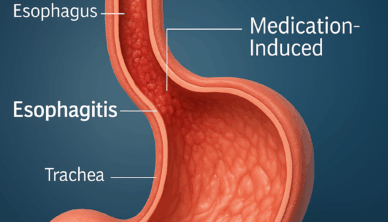
Esophagitis refers to inflammation of the oesophagus—the muscular tube that carries food from your mouth to your stomach. It can result from acid reflux, infections, medications, or allergies. If left untreated, esophagitis may lead to complications such as ulcers, scarring, or difficulty swallowing.
At The New Foscote Hospital in Banbury, our expert gastroenterology team provides comprehensive diagnosis and care for patients experiencing oesophageal discomfort or related symptoms.
Causes of Esophagitis
Esophagitis may be caused by:
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): The most common cause; stomach acid frequently flows back into the oesophagus, irritating the lining.
- Infections: Particularly in people with weakened immune systems (e.g., due to HIV or chemotherapy).
- Medication-induced: Certain tablets can irritate the oesophagus if not swallowed properly (e.g., antibiotics, NSAIDs).
- Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A chronic immune system disease linked to food allergies.
- Radiation or chemical injury: Rare but possible with cancer treatment or ingestion of corrosive substances.
Symptoms of Esophagitis
Patients may experience:
- Pain or difficulty when swallowing
- Chest pain (especially behind the breastbone)
- Acid reflux or heartburn
- A sensation of food being stuck in the throat
- Coughing or sore throat
- Nausea or vomiting (in some cases)
If you notice persistent symptoms, early consultation can prevent further complications.
Diagnosis at The New Foscote Hospital
We offer same-day diagnostics to ensure prompt evaluation. Tests may include:
- Barium swallow X-ray: Highlights abnormalities in the oesophageal structure.
- Upper endoscopy (gastroscopy): A thin, flexible tube with a camera is used to examine the oesophagus.
- Biopsy: Small tissue samples may be taken during endoscopy to identify the underlying cause.
- pH monitoring: Measures acid levels in the oesophagus.
Treatment Options
Your treatment plan will depend on the underlying cause:
- Acid reflux–related esophagitis: Treated with antacids, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), or lifestyle changes (diet, weight loss, avoiding trigger foods).
- Infectious esophagitis: Antiviral, antifungal, or antibiotic medication based on the infection.
- Eosinophilic esophagitis: Managed with dietary changes, corticosteroids, or allergy treatment.
- Medication-induced: Changing medications or improving swallowing techniques.
- Severe cases: May require dilation of the oesophagus or surgery if strictures have formed.

Why Choose The New Foscote Hospital?
- Personalised aftercare and dietary support
- Consultant-led care with short waiting times
- Access to advanced diagnostic tools and imaging
- Multidisciplinary approach for complex cases
- On-site endoscopy and recovery facilities
If you are experiencing symptoms of esophagitis, our team is here to help.
Contact The New Foscote Hospital today to book a consultation and start your journey toward recovery.
21 May 2025


